We will learn how request.get method works by making the function which is aiming at sort blogs by different category. BUt in this project we will use different members as the different blog categories. Project link
1. Create category in db / models.py
from django.db import models
class Caselog(models.Model):
caseid = models.CharField(null=True, blank=True,max_length=200)
orgnization = models.CharField(null=True, blank=True,max_length=200)
problem = models.CharField(null=True, blank=True,max_length=200)
solution = models.TextField(null=True, blank=True)
# handleby = models.CharField(max_length=100, default='',
# choices=((u'Andy',u'Andy'),(u'David',u'David')))
MEMBER = (
('david','David'),
('andy','Andy'),
)
handleby = models.CharField(null=True, blank=True, max_length=5, choices=MEMBER)
date = models.DateField(null=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.caseid
Explanation about the codes above.
choices is a dropdown list .
MEMBER = (
('david','David'),
('andy','Andy'),
lower letters are the attribute that will get in url, and the capital letters will be shown in the admin console when we create a new caselog and could chose a member by the dropdown list.
Then, evenytime, if any changes in the models.py, run the command below.
python manege.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
2. views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from webapp.models import Caselog
def default(request):
print('==='*30)
print(request)
print('==='*30)
print(dir(request))
print('==='*30)
print(type(request))
print('==='*30)
queryset = request.GET.get('handleby')
print(queryset)
if queryset:
caselog_list = Caselog.objects.filter(handleby=queryset)
else:
caselog_list = Caselog.objects.all()
context = {
'Caselog': caselog_list
}
return render(request, 'default.html', context)
The explanation.
-
when we print(request), we will get
WSGIRequest: GET 'default' -
request.GET.get('handleby'), ‘GET’ is the request method we will use, just like the ‘GET’above, get(‘handleby’) means we will only get the ‘handleby’ in the url even the url has many attributes.For testing print(queryset), input the url as 127.0.0.1:8000/default/?handleby=123456, and it will shows ‘123456’, which is the value of this attribute ‘handleby’ we just input.
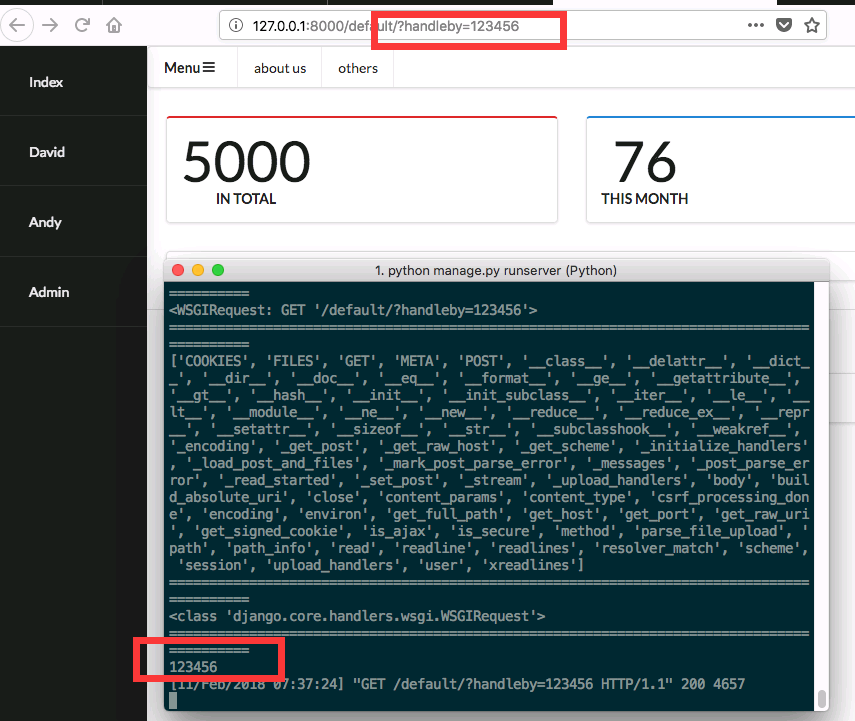
-
So, all the same. we can make an url with a spicific ‘handleby’ attribute to sort data by using GET method.
Let’s go on to make it in real. if there’s a attribute,Then sort data by the attribute. else get objects all without any sorting conditions.
queryset = request.GET.get('handleby') if queryset: caselog_list = Caselog.objects.filter(handleby=queryset) else: caselog_list = Caselog.objects.all()
3. templates
Let’s make a html button to input data sorting attribute link.
<div class="ui thin visible left sidebar inverted vertical menu" id="sidebar">
<div class="item">
<a class="item" href="/default">Index</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a class="item" href="?handleby=david">David</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a class="item" href="?handleby=andy">Andy</a>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a class="item" href="/admin">Admin</a>
</div>
</div>
yay!!! finished.


