To give a detailed introduction about request.post. we will make the comment fuction to show how request.post works.
-
Create comment database in models.py
-
views.py / form.py
-
template
-
ValidationError
1. Caselog details html page
Create template log_detail.html and define a url for this page in urls.py.
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from webapp.views import default, detail
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^default/', default, name='default'),
url(r'^detail/', detail, name='detail'),
]
2. Create comment model / db
class Comment(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(null=True, blank=True,max_length=20)
comment = models.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.comment
Use the commands to generate/create db.
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
3. views.py
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponseRedirect, redirect
from webapp.models import Caselog, Comment
from webapp.form import CommentForm # This function could define here.
def detail(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
form = CommentForm #创建表单
if request.method == 'POST':
form = CommentForm(request.POST) #绑定表单,实现数据校验
if form.is_valid():
name = form.cleaned_data['name']
comment = form.cleaned_data['comment']
c = Comment(name = name, comment = comment)
c.save()
return redirect(to='detail') # 'name' in urls
context = {}
comment_list = Comment.objects.all()
context['comment_list'] = comment_list
context['form'] = form
return render(request, 'log_detail.html', context)
Create form.py
from django import forms
class CommentForm(forms.Form):
name = forms.CharField(max_length=50)
comment = forms.CharField()
models.Model may look same as forms.Form, BUT totally different!!!
4. Template log_detail.html
Rewirte html page by django template language.
{% load static%}
"{% static `css\semantic.css` &}"
Using the commands above to change the static path before moving on.
<div class="ui comments">
{% for comment in comment_list %}
<div class="comment">
<div class="avatar">
<img src="http://semantic-ui.com/images/avatar/small/matt.jpg" alt="" />
</div>
<div class="content">
<a href="#" class="author">{{ comment.name }}</a>
<div class="metadata">
<div class="date">2 days ago</div>
</div>
<p class="text" style="font-family: 'Raleway', sans-serif;">
{{ comment.comment }}
</p>
</div>
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
<form class="ui form" action="" method="post">
- <div class="field">
- <label> name</label>
- <input type="text" name="name" value="">
- </div>
- <div class="field">
- <label>comment</label>
- <textarea></textarea>
- </div>
+ # {{ form }}
+ {{ form.as_p }}
+ {{ csrf_token }}
<button type="submit" class="ui blue button" >Click</button>
</form>
Explanation.
form.as_pmeans wrap each field of form in a<p></p>
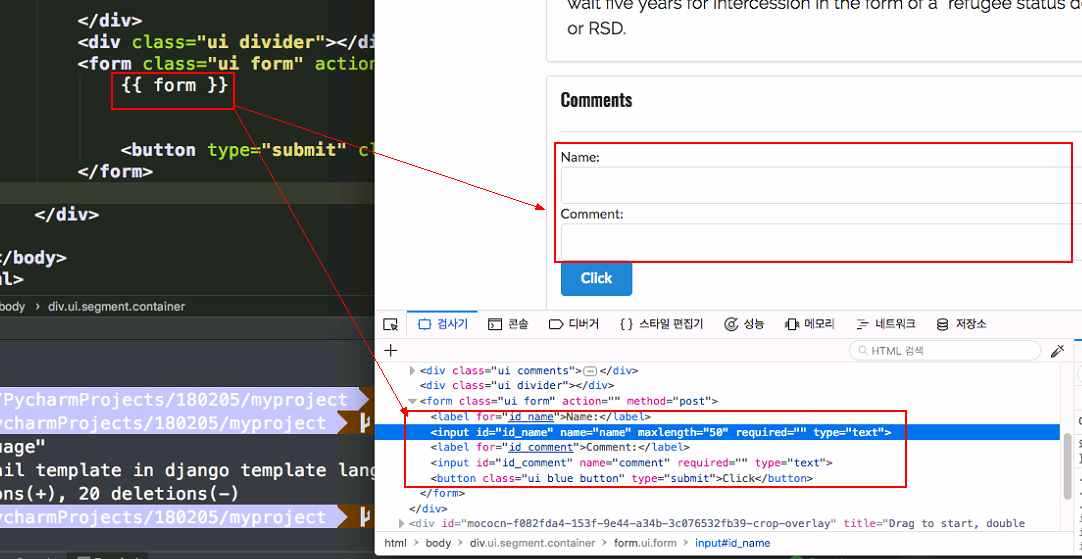
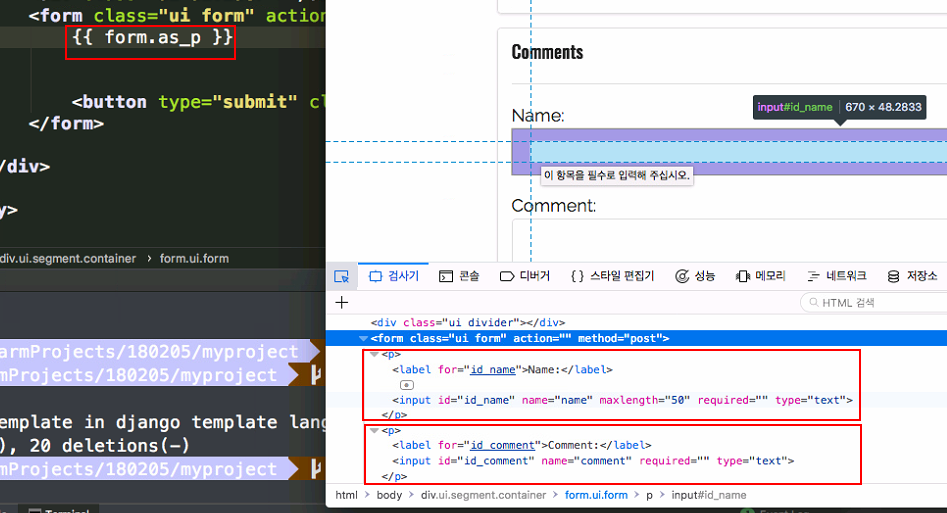
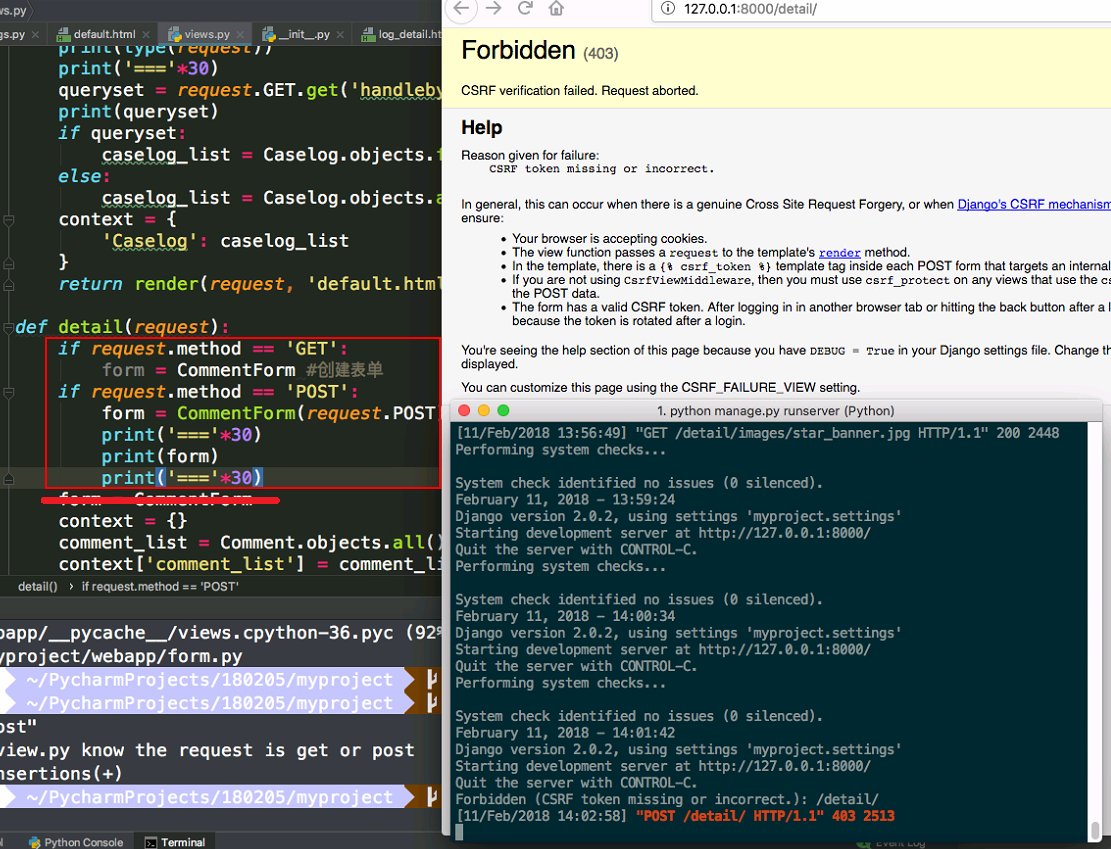
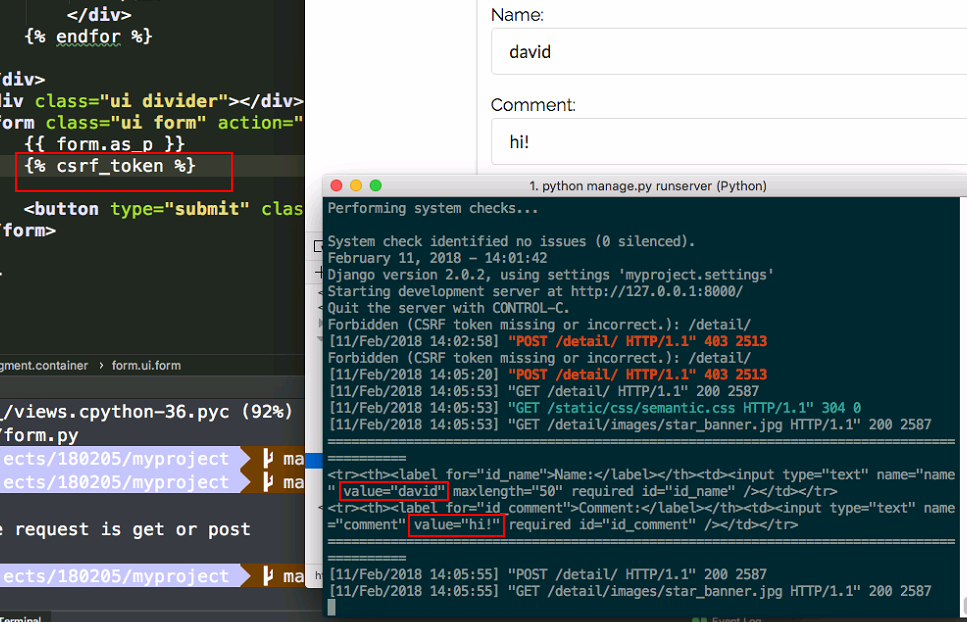
- when we try to submit the form, then csrf error occurred.
csrf_tokenmeans let the broswer know you are you.
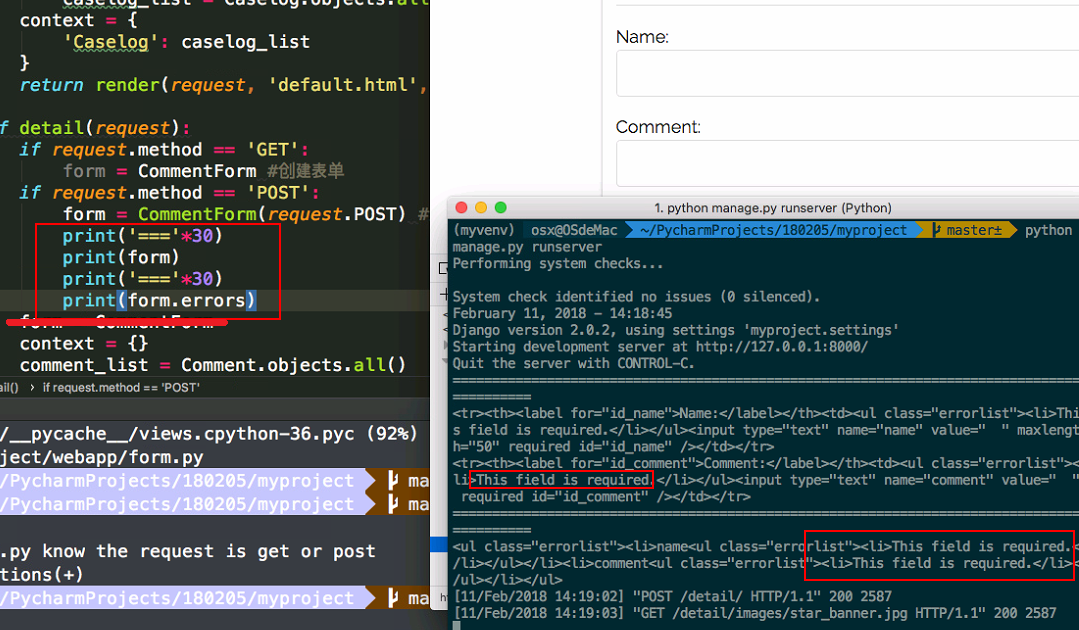
- Django.form validates error automatically Use print(form.error) to have a look at what the error is. Although we will make validation conditions by ourself.
if request.method == 'POST':
form = CommentForm(request.POST) #绑定表单,实现数据校验
print('==='*30)
print(form)
print('==='*30)
context = {}
comment_list = Comment.objects.all()
- Save the data that we input in the form
if request.method == 'POST':
form = CommentForm(request.POST) #绑定表单,实现数据校验
+ if form.is_valid():
+ name = form.cleaned_data['name']
+ comment = form.cleaned_data['comment']
+ c = Comment(name = name, comment = comment)
+ c.save()
+ return redirect(to='detail') # 'name' in urls
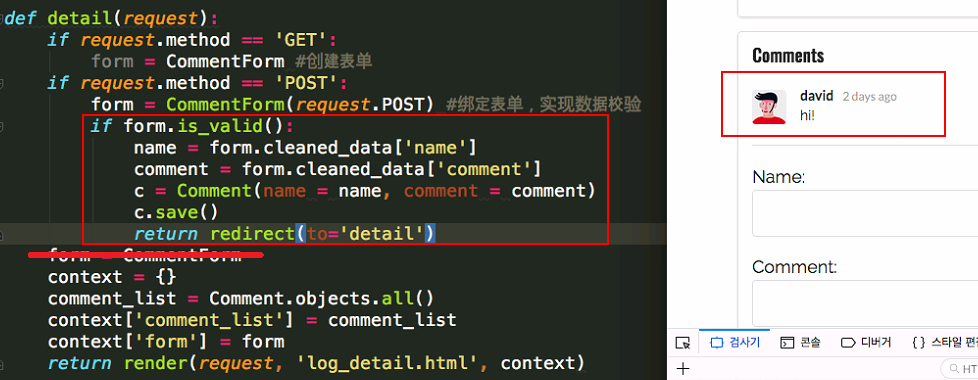
By Now, comment function can work well.
5. Customize django.form ValidationError
5.1 form.py
from django import forms
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
def words_validator(comment):
if len(comment) < 4:
raise ValidationError('Not Enough Letters')
def comment_validator(comment):
if 'a' in comment:
raise ValidationError('Do Not Use the Word!')
class CommentForm(forms.Form):
name = forms.CharField(max_length=50)
comment = forms.CharField(
widget=forms.Textarea(), # change CharField to TextField
error_messages={
'required': 'why no words?' # pop up error_messages
},
validators=[words_validator, comment_validator] # Customized error conditions
)
5.2 log_detail.html, customize render form.
<form class="ui form" action="" method="post">
- {{ form.as_p }}
+ # {% for field in form %}
+ # <div class="field">
+ # {{ field.label }}
+ # {{ field }}
+ # </div>
+ # {% endfor %}
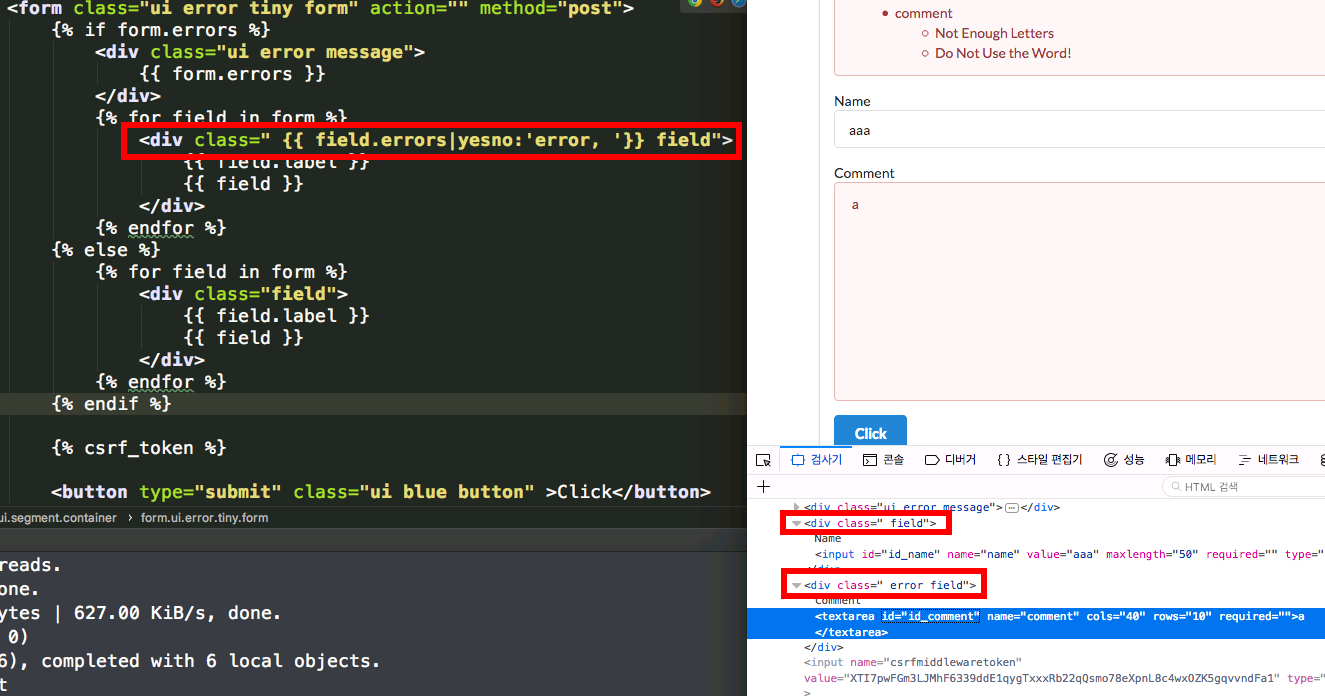
{% if form.errors %}
<div class="ui error message">
{{ form.errors }}
</div>
{% for field in form %}
<div class=" {{ field.errors|yesno:'error, '}} field">
{{ field.label }}
{{ field }}
</div>
{% endfor %}
{% else %}
{% for field in form %}
<div class="field">
{{ field.label }}
{{ field }}
</div>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{% csrf_token %}
<button type="submit" class="ui blue button" >Click</button>
- The key point is that the error field will have a error css of form,
<div class=" field">which means if field.errors is yes, then<div class=" error field">, or it will be<div class=" field">.